Probability Distribution of Rolling Two Dice
The probability distribution is. Due to a planned power outage on Friday 114 between 8am-1pm PST some services may be impacted.
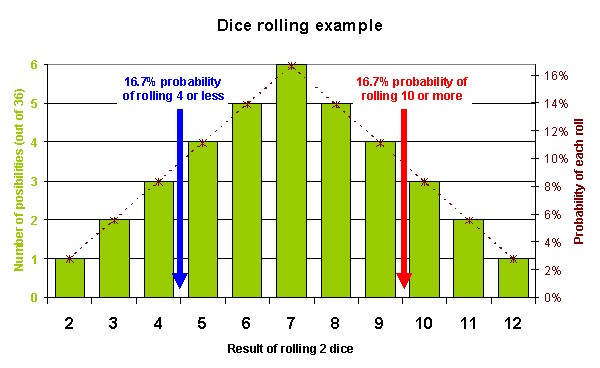
If two dice are thrown together the odds of getting a seven are the highest at 636 followed by six and eight with equal odds of 536 1389 then five and nine with odds of 436 1111 and so on.
. This video we create he probability distribution table for the sum of two dice. Instead we get an empirical distribution that differs from the theoretical one. That is X 123456 and Y 123456.
We discovered that when we randomly toss two dice we rarely if ever get the theoretical distribution. Now we can look at random variables based on this probability experiment. For n 6 this gives 7 2.
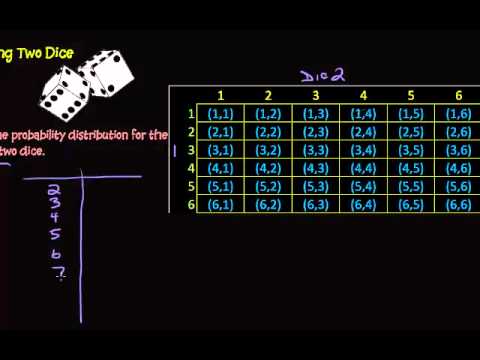
Here Pr stands for probability the event is written in the square brackets and Y needs to be defined as the sum of 2 die rolls. The 36 possible outcomes are as follows. Sample Questions Question 1.
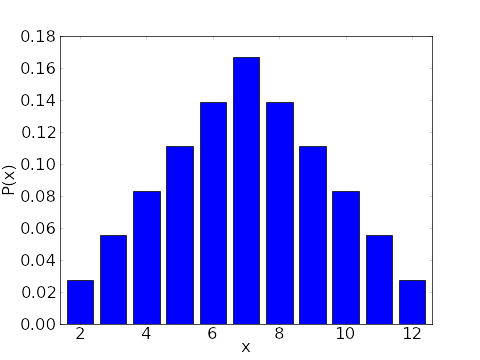
A bar chart illustrating the probability distribution for a random variable X that is given by the sum of the result of rolling two six-sided dice. Probability As a percentage this is 833 percent. 1 6 stands for getting 1 on the first die and and 6 on.
Of all possible outcomes. When we used the program DICETOSS we saw that most often if we kept rolling our whole distribution of observed frequencies came fairly close to the theoretical probabilities. For example x¹x⁶ x⁶x¹x² x⁵ x⁵x² x⁴ x³ x³x⁴ x⁷.
When counting up the outcomes that result in 3 we find only two 2 1 21 and 1 2 12. 7 rows To determine the probability of rolling any one of the numbers on the die we divide the event. Probability distribution of rolling two dice.
There are 36 total possible outcomes 6 for each individual dice and we take the product for the total number. As a review heres the probability of rolling a 2 on our mathematical six-sided die. 16 61 25 52 43 34.
Let X be the Random Variable that represents the sum of the two die then the probability distribution of X is. For two dice the probability of getting a total value of 4 or 12 is 136 I ignore the case of 2 and 3 since one of the dice has to have a value of 1. Sum of 3 fair dice k 3 1 Oe 15e 2 le 25e 27e Sum of 4 fair dice 4 t eee e e e 20e 146e 1296.
This is the probability distribution of the sum of two fair dice. The probability is the number of outcomes with a total of 3 divided by the total number of outcomes or frac 2 36 approx 006 362. PtextrmFirst roll 2 and Second roll 6 P textrmFirst roll is 2 times P textrmSecond roll is 6 frac136.
From this we can draw a table summarising the number of times a possible outcome can occur. A natural random variable to consider is. Prob 2 d6 Fraction 1 6 And here is the probability of rolling an even number.
This gives a probability of frac2n-1n2. 6 x 6. Here we have the.
We have previously discussed the probability experiment of rolling two 6-sided dice and its sample space. Two dice are rolled. X sum of the two dice You will construct the probability distribution of this random variable.
The probability of a 5 or 11 WITHOUT a dice having a value of one is 118 6 or 10 WITHOUT a dice having a. Let us understand the sample space of rolling two dice. The probability of an event number of favorable outcomes total number of outcomes.
The probability of rolling a 1 is 0 since there are no outcomes in the sample space that can satisfy the. Only 1 outcome satisfies the event. Probability distribution for the sum of two six-sided dice.
Now weve counted the case nn twice so subtracting this off we see there are 2n-1 possibilities. If it appears on the first die there are n choices for the second die. When we roll two dice simultaneously the probability that the first roll is 2 and the second is 6.
Therefore probability 6 36 0167 167 percent. Subtracting n 2 2 n 1 4 yields n 2 1 12. Mallika rolled a dice then find the probability that Mallika will get a prime number on the dice.
Similarly for the case where n appears on the second die. P textrmFirst roll is 2 frac16. Return n 2 0 probis_even d6 Fraction 1 2 Now lets generate the outcomes from rolling two fair independent dice using the Cartesian product.
Find the Probability of the sum of scores is an odd number. The mgf M t of the sum Sfork 34 5 is similarly obtained from equation 4. P textrmSecond roll is 6 frac16.
Suppose we want our largest roll to be n. Probability of sum of an even numbers 18 36 1 2. The probability of rolling the same value on each die - while the chance of getting a particular value on a single die is p we only need to multiply this probability by itself as many times as the number of dice.
When two dice are rolled total no. Here is the same information in table form. Two dices are rolled at a time.
The probability of rolling a 2 is 1 36. In other words the probability P equals. For example 4 3 stands for getting 4 on the first die and and 3 on the second die.
P x 1 36 if x 2 12 2 36 1 18 if x 3 11 3 36 1 12 if x 4 10 4 36 1 9 if x 5 9 5 36 if x 6 8 6 36 1 6 if x 7 0 otherwise. Here the sample space is given when two dice are rolled. For two dice 7 is the most likely result with six ways to achieve it.
For n 6 this gives 35 12. These all represent a total sum of 7 and therefore the probability of rolling a 7 with 2 dice is a combination of the probability of rolling any of these. The variance of a single die whose faces vary from 1 to n is the mean of the squares minus the square of the mean The sum of the squares from 1 to n is 2 n 3 3 n 2 n 6 so the mean is 2 n 2 3 n 1 6.
It is for two dice rolled simultaneously or one after another classic 6-sided dice.

Image Probability Distribution For The Sum Of Two Six Sided Dice Math Insight

Probability Why Is The Sum Of The Rolls Of Two Dices A Binomial Distribution What Is Defined As A Success In This Experiment Mathematics Stack Exchange
No comments for "Probability Distribution of Rolling Two Dice"
Post a Comment